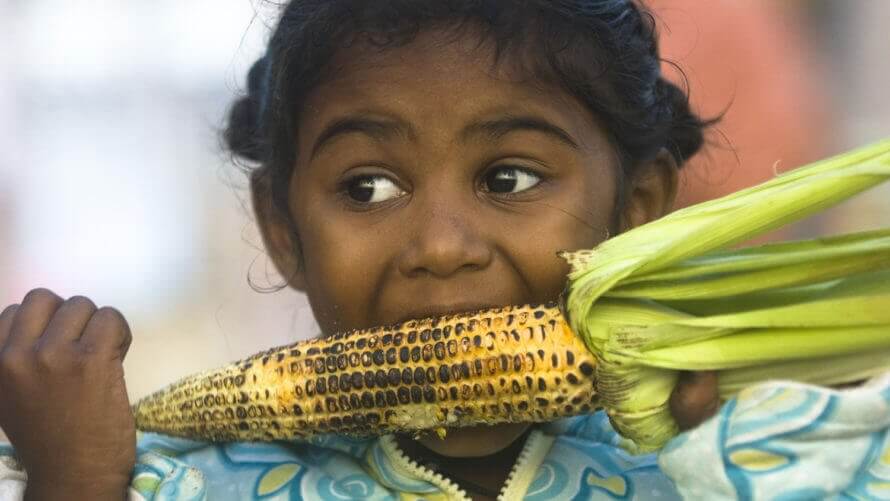
[Molecular biologist Mike] Daly has been investigating ways to apply the lessons learned from this bacteria’s unique radiation resistance to the production of faster, cheaper, and safer vaccines.
Earlier this year, Daly and his group at USU published the results of their efforts to produce an inactivated polio vaccine.
…
“If you can grow-up your pathogen (whatever it is), if you mix it in with these manganese antioxidants [found in extremophiles],” Daly said, “you should be able to obliterate the genome, whether it’s RNA or DNA, and render it completely non-infective and sterile, while at the same time preserving all the structures and peptides, all the ligands and all the things that make up the surface of the virus or bacteria. Then you’ve sort of got like a ghost of what the real thing is.”
…
Across the gamut of theoretically promising vaccine development concepts, a lot of laborious tinkering tends to crop up in practice: Strains of a virus need to be identified and compared; genomes need to be mapped to find the code for those most useful surface proteins; inactivation methods need to be tweaked, adjusted, or wholly rethought for a given virus. Essentially, what Daly’s team has done is figure out a way to sidestep most of this to make a classic inactivated whole virus vaccine, very quickly and with negligible damage to the critical antigenic proteins on the bug’s surface.