If you believe product labels and inflammatory headlines it seems like almost everyone must be doubled over with celiac disease. Numerous websites, celebrity doctors, and internet personalities have concluded that this disorder is irrefutably caused by human meddling in wheat genetics. After all, Mother Nature would never make something harmful.
But new research indicates that the celiac-inducing factors in wheat are actually historical genetic remnants found in older “heirloom” types as well as modern varieties. The work was published recently in the journal Food Chemistry.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects about one percent of the population. The symptoms are related to inflammation in the digestive tract, induced by any one of several small proteins found in cereals. These are commonly referred to as “glutens” but specifically are known as gliadin and glutenin. They are a natural presence in wheat, rye and barley.
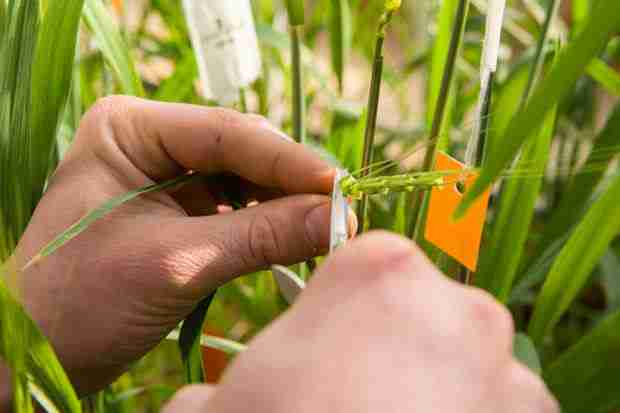

Several groups have examined the abundance of glutenin and gliadin in modern wheat and older accessions, including the landraces cultivated by ancient peoples. Some of the work has demonstrated an increased level of immunogenic factors in the recent varieties, consistent with the notion that celiac symptoms may be related to modern breeding. Others have shown exactly the opposite, showing that ancient wheat possesses higher levels of gluten.
The present work examined wheat bred and grown in North Dakota over the last 110 years. The authors used a variety of techniques to quantify the epitopes present in older and newer varieties. Epitopes are the signatures in specific proteins that trigger immune response.
The result of the most recent work — there is no pattern. Some ancient varieties have high levels, some have low levels. Some modern varieties have high levels, some have low levels.
So why do different research groups see different results? It is quite possible that they all do beautiful work and are all correct.
In all of the research reports, different varieties were examined, different methods of quantitation were used. and plants were grown in different environments. We know that accumulation of different proteins can be profoundly influenced by even small changes in the environment. Together, all of these factors might explain why there is no clear association between gluten presence and wheat improvement, and why there is disagreement between studies.
The take-home message is that gluten, and its contribution to human digestive ills, does not appear to be a product of modern breeding. While crop improvements like better yields, disease resistance, and the ability to survive weather extremes are easily measured, they did not happen with a parallel increase in gluten proteins.
While it is trendy to blame human participation in plant genetics as the root of all food problems, the data don’t match the allegation. Wheat’s rich genetic history has provided the molecular bones of pasta and bread, and a profitable crop for the farmers that grow it. For the 99% of us that are not celiac-sensitive this is very good news.
For the 1% that suffer from celiac disease — hope is on the horizon. New gene-editing techniques are being used to remove the problematic epitopes in wheat. In the near future celiac-safe wheat will be commonplace.
The plants that Mother Nature produced possess compounds that negatively affect some consumers. Plant breeding did not make them worse. Quite the opposite, new technology is helping make these products safe for everyone. It is again an important testament to the power of plant breeding and importance of embracing the next wave of technology in crop improvement.
Kevin Folta is a professor and chair of the Horticultural Sciences Department at the University of Florida. He teaches science communication workshops for scientists and ag professionals, and hosts the weekly podcast Talking Biotech. Follow him on twitter @kevinfolta.
This article was originally published at RealClearScience as “Wheat Breeding Not to Blame for Celiac Disease” and has been republished here with permission.